
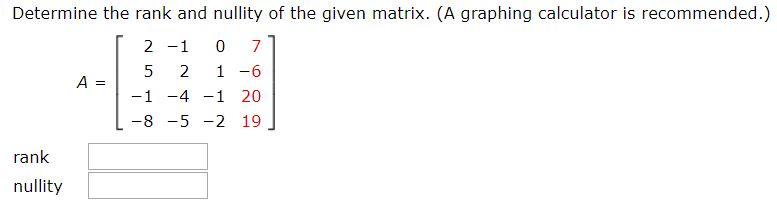
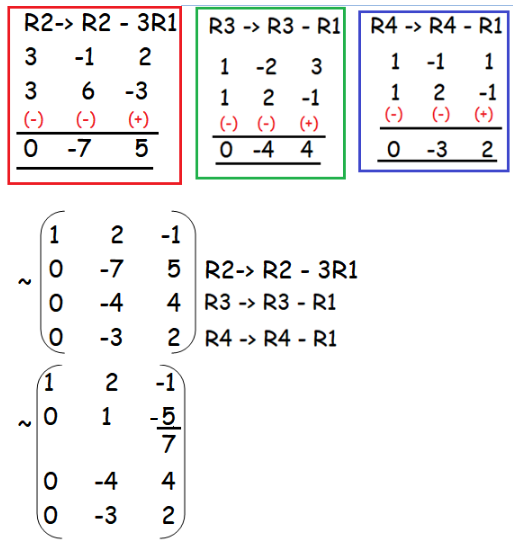
Our experiments show improvements in prediction accuracy over classical approaches for recommendation tasks. Rank of Matrix on the basis of Minor of Matrix The highest order of non-zero minor of a matrix is said to be the rank of a matrix. We analyze the accuracy of the proposed local low-rank modeling. We propose a new matrix approximation model where we assume instead that the matrix is locally of low-rank, leading to a representation of the observed matrix as a weighted sum of low-rank matrices. Here are some of the connections between the rank of a matrix and the number of solutions to a system of linear equations. The rank is at least 1, except for a zero matrix (a matrix made of all zeros) whose rank is 0. A prevalent assumption in constructing matrix approximations is that the partially observed matrix is of low-rank. Example: for a 2×4 matrix the rank can't be larger than 2 When the rank equals the smallest dimension it is called 'full rank', a smaller rank is called 'rank deficient'. Therefore, to determine the rank of a matrix, the matrix needs to transform to the echelon form to identify the number of non-zero rows in the matrix. The rank is at least 1, except for a zero matrix (a matrix made of all zeros) whose rank is 0. The rank of a matrix is denoted by the number of rows and columns that are independent of each other. When the rank equals the smallest dimension it is called 'full rank', a smaller rank is called 'rank deficient'. For matrix A, rank is 2 (row vector a1 and a2 are linearly.
#RANK OF A MATRIX FULL#
= īT - Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine LearningĭP - Proceedings of Machine Learning ResearchĪB - Matrix approximation is a common tool in recommendation systems, text mining, and computer vision. What is full rank matrix example Example: for a 2×4 matrix the rank cant be larger than 2. Rank of Matrix Maximum number of linearly independent rows in a matrix (or linearly independent columns) is called Rank of that matrix.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
